How does planning poker work – Steps in detail. This is an agile planning poker scrum activity. Every estimator will have a deck of cards and begin with the exercise. Figure 2: Steps involved in a planning poker game The participants are the moderators in the scrum poker. Planning Poker is a consensus-based technique for estimation, mostly used to estimate effort or relative size of development goals in software product development. Planning Poker is done with story points, ideal days, or any other estimating units. The Scrum Master, Product Owner, and the development team participate in Planning Poker activity.
Agile Concepts: Estimating and Planning Poker
Planning Poker (also known as Scrum Poker) is a very popular technique proposed in 2002 by James Grenning.Each player uses a set of cards with Fibonacci sequence numbers on it to estimate the overall effort of a task in Story Points. Planning Poker procedure. Take in mind that with great popularity came multiple variations of this technique, each team tend to adapt it for their needs. Question 1: There seems to be no frame of reference to compare this session to past planning poker sessions, though. There should be. Have your scrum master bring in one medium sized story from the previous sprint. You then have a reference point from which to start. A Story Point (SP) is a relative unit of measure, decided upon and used by individual Scrum teams, to provide relative estimates of effort for completing requirements. What is Planning Poker?3.
Most Agile frameworks include some form of estimation*. Estimating the relative size of stories in terms of effort/time can help a team to decide how many of the highest priority stories from the product backlog can be taken on in a single sprint.
Estimating is also used to measure the velocity of a team (the amount of work it gets through per sprint), helping the business to forecast and budget product development.
Estimating using story points
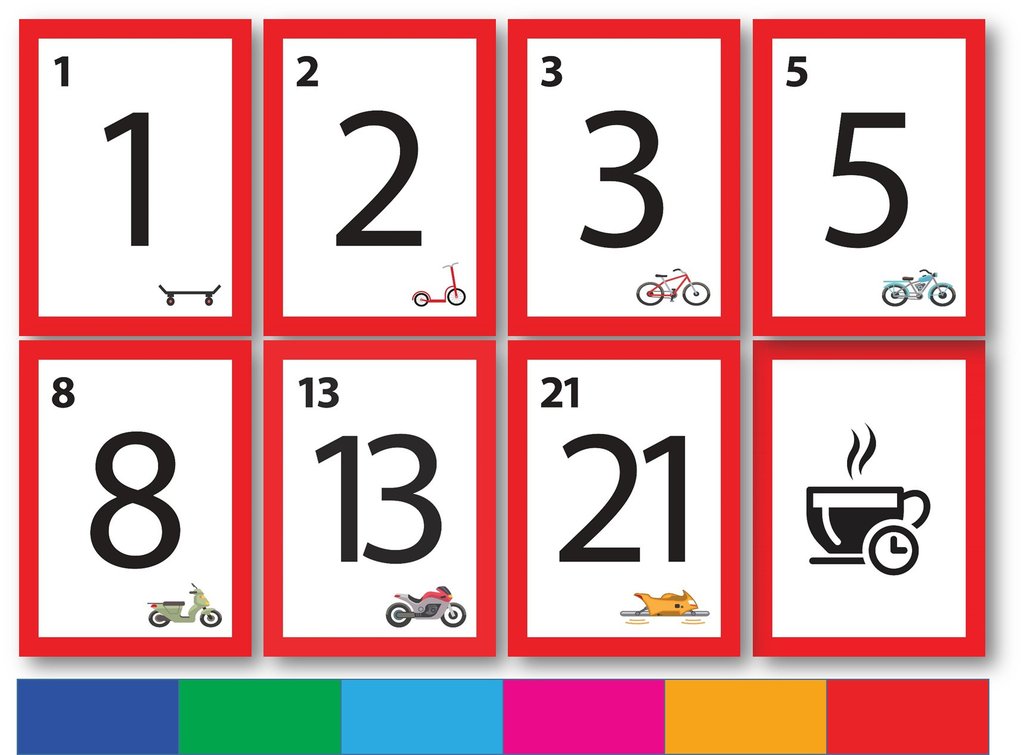
The most common way of estimating the size of user stories in Scrum is by allocating story points. Story points are just numbers drawn from a pool of numbers of a set size e.g. a story could have 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40 or 100 story points.
The reason for using a Fibonacci-like sequence of numbers is to encourage stories to be estimated relatively (e.g. that story looks like it requires about twice the effort for a story we've already agreed is a 2 so it's probably a 5) and to emphasise that the larger the story, the more uncertain the estimate.
Who estimates?
A Scrum team will estimate story points during backlog refinement or perhaps as part of a dedicated session. It's essential that the whole team is involved in the process of estimation so that the estimates are made by the people who will actually be doing the work and are therefore as accurate as possible.
When a story is ready for estimation – i.e. when it is small enough to fit within a single sprint and when the acceptance criteria have been agreed by the scrum team – the team then discusses its relative size and reaches consensus over how many story points of effort it requires.
Stories may be estimated before these criteria are met but should be revisited.
The most common way to do this is Scrum is by playing planning poker.
Planning poker
In planning poker each member of the team gets a set of playing cards with the allowable story points printed on the front as well as extra cards for don't know (?), infinity or, sometimes, to indicate it's time for a coffee break.
Once the story is ready to be estimated, there is a round of voting. At the same time, all team members hold up the card which corresponds to their estimate.
If all the team members agree then the story is given that number of points and the team moves on.
If there are discrepancies then the ScrumMaster facilitates a discussion where team members can further explore what's required, investigate acceptance criteria further etc. There is then another round of voting and this repeats until consensus is achieved. Slot angel login app.
It's particularly important to discuss the lowest and highest estimates from the team, this often leads to clarifications with the Product Owner and an updated set of assumptions for the estimate (which should be captured).
Estimating controversy
*Estimating is a hot button topic in Agile right now. Some argue that estimating is a process of the kind that Agile should be pushing to the background in favour of individuals and interactions and also a form of contracting which should be de-emphasised in favour of customer collaboration. They argue that estimating how long it will take to deliver a product – the development of which will be inherently unpredictable – based on guesswork is a useless activity which fits the incremental model better than it fits a purely iterative one (see Agile vs Waterfall).
The reality is in real world scenarios it is almost always critically important to have ability to forward plan. Story points and velocity give a pragmatic way to do this and often on the projects where Scrum is used there is a good understanding of the type of work being done and the estimates are of a good standard.
Using techniques like triangulation and reference stories aid the process.
Whether you think it's a futile box-ticking exercise or a useful way for businesses to plan product development, it's important as practitioners that we understand how to estimate effectively.
What is Planning Poker?
Planning Poker is an agile estimating and planning technique that is consensus based. To start a poker planning session, the product owner or customer reads an agile user story or describes a feature to the estimators.
Each estimator is holding a deck of Planning Poker cards with values like 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40 and 100, which is the sequence we recommend. The values represent the number of story points, ideal days, or other units in which the team estimates.
The estimators discuss the feature, asking questions of the product owner as needed. When the feature has been fully discussed, each estimator privately selects one card to represent his or her estimate. All cards are then revealed at the same time.
If all estimators selected the same value, that becomes the estimate. If not, the estimators discuss their estimates. The high and low estimators should especially share their reasons. After further discussion, each estimator reselects an estimate card, and all cards are again revealed at the same time.
The poker planning process is repeated until consensus is achieved or until the estimators decide that agile estimating and planning of a particular item needs to be deferred until additional information can be acquired.
When should we engage in Planning Poker?
Most teams will hold a Planning Poker session shortly after an initial product backlog is written. This session (which may be spread over multiple days) is used to create initial estimates useful in scoping or sizing the project.
Because product backlog items (usually in the form of user stories) will continue to be added throughout the project, most teams will find it helpful to conduct subsequent agile estimating and planning sessions once per iteration. Usually this is done a few days before the end of the iteration and immediately following a daily standup, since the whole team is together at that time anyway.
How does poker planning work with a distributed team?
Simple: go to PlanningPoker.com. Mountain Goat Software helped develop that website to offer it as a free resource to the agile community. A product owner, ScrumMaster or agile coach can log in and preload a set of items to be estimated. A private URL can then be shared with estimators who log in and join a conference call or Skype session. Agile estimating and planning then proceeds as it would in person.
Does Planning Poker work?
Absolutely. Teams estimating with Planning Poker consistently report that they arrive at more accurate estimates than with any technique they'd used before.
Welcome to Pokerchipswholesale.com. We sell poker chips at amazingly low prices. Our poker chip selection is excellent and our prices are the best in the industry. We sell clay poker chips, clay composite poker chips and plastic poker chips. Poker Chip Mania offers one of the Largest Selections of Poker Chips and Supplies at the Lowest Prices since 2006. All Chip Sets can be Customized by YOU! - You select how many of what colors you want in your set. Don't settle for a poker chip set that you can't. Ultimate Poker Supplies provides high quality poker chips, chip cases and carousels, card shufflers and poker accessories at great wholesale and cheap prices. Ultimate Poker Supplies carries poker, clay, casino & customized chips, KEM & COPAG cards, shufflers, cases, DVD's, and Blackjack supplies. Poker chip suppliers list.
One reason Planning Poker leads to better estimates is because it brings together multiple expert opinions. Because these experts form a cross-functional team from all disciplines on a software project, they are better suited to the estimation task than anyone else.
Scrum Planning Poker
After completing a thorough review of the literature on software estimation, Magne Jørgensen, Ph.D., of the Simula Research Lab concluded that 'the people most competent in solving the task should estimate it.'
Second, a lively dialogue ensues during poker planning, and estimators are called upon by their peers to justify their estimates. Researchers have found that this improves estimate accuracy, especially on items with a lot of uncertainty as we find on most software projects.

Further, being asked to justify estimates has also been shown to result in estimates that better compensate for missing information. This is important on an agile project because the user stories being estimated are often intentionally vague.
Scrum Story Points Definition
Additionally, studies have shown that averaging individual estimates during agile estimating and planning leads to better results as do group discussions of estimates.
How can I get Planning Poker cards?

Stories may be estimated before these criteria are met but should be revisited.
The most common way to do this is Scrum is by playing planning poker.
Planning poker
In planning poker each member of the team gets a set of playing cards with the allowable story points printed on the front as well as extra cards for don't know (?), infinity or, sometimes, to indicate it's time for a coffee break.
Once the story is ready to be estimated, there is a round of voting. At the same time, all team members hold up the card which corresponds to their estimate.
If all the team members agree then the story is given that number of points and the team moves on.
If there are discrepancies then the ScrumMaster facilitates a discussion where team members can further explore what's required, investigate acceptance criteria further etc. There is then another round of voting and this repeats until consensus is achieved. Slot angel login app.
It's particularly important to discuss the lowest and highest estimates from the team, this often leads to clarifications with the Product Owner and an updated set of assumptions for the estimate (which should be captured).
Estimating controversy
*Estimating is a hot button topic in Agile right now. Some argue that estimating is a process of the kind that Agile should be pushing to the background in favour of individuals and interactions and also a form of contracting which should be de-emphasised in favour of customer collaboration. They argue that estimating how long it will take to deliver a product – the development of which will be inherently unpredictable – based on guesswork is a useless activity which fits the incremental model better than it fits a purely iterative one (see Agile vs Waterfall).
The reality is in real world scenarios it is almost always critically important to have ability to forward plan. Story points and velocity give a pragmatic way to do this and often on the projects where Scrum is used there is a good understanding of the type of work being done and the estimates are of a good standard.
Using techniques like triangulation and reference stories aid the process.
Whether you think it's a futile box-ticking exercise or a useful way for businesses to plan product development, it's important as practitioners that we understand how to estimate effectively.
What is Planning Poker?
Planning Poker is an agile estimating and planning technique that is consensus based. To start a poker planning session, the product owner or customer reads an agile user story or describes a feature to the estimators.
Each estimator is holding a deck of Planning Poker cards with values like 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40 and 100, which is the sequence we recommend. The values represent the number of story points, ideal days, or other units in which the team estimates.
The estimators discuss the feature, asking questions of the product owner as needed. When the feature has been fully discussed, each estimator privately selects one card to represent his or her estimate. All cards are then revealed at the same time.
If all estimators selected the same value, that becomes the estimate. If not, the estimators discuss their estimates. The high and low estimators should especially share their reasons. After further discussion, each estimator reselects an estimate card, and all cards are again revealed at the same time.
The poker planning process is repeated until consensus is achieved or until the estimators decide that agile estimating and planning of a particular item needs to be deferred until additional information can be acquired.
When should we engage in Planning Poker?
Most teams will hold a Planning Poker session shortly after an initial product backlog is written. This session (which may be spread over multiple days) is used to create initial estimates useful in scoping or sizing the project.
Because product backlog items (usually in the form of user stories) will continue to be added throughout the project, most teams will find it helpful to conduct subsequent agile estimating and planning sessions once per iteration. Usually this is done a few days before the end of the iteration and immediately following a daily standup, since the whole team is together at that time anyway.
How does poker planning work with a distributed team?
Simple: go to PlanningPoker.com. Mountain Goat Software helped develop that website to offer it as a free resource to the agile community. A product owner, ScrumMaster or agile coach can log in and preload a set of items to be estimated. A private URL can then be shared with estimators who log in and join a conference call or Skype session. Agile estimating and planning then proceeds as it would in person.
Does Planning Poker work?
Absolutely. Teams estimating with Planning Poker consistently report that they arrive at more accurate estimates than with any technique they'd used before.
Welcome to Pokerchipswholesale.com. We sell poker chips at amazingly low prices. Our poker chip selection is excellent and our prices are the best in the industry. We sell clay poker chips, clay composite poker chips and plastic poker chips. Poker Chip Mania offers one of the Largest Selections of Poker Chips and Supplies at the Lowest Prices since 2006. All Chip Sets can be Customized by YOU! - You select how many of what colors you want in your set. Don't settle for a poker chip set that you can't. Ultimate Poker Supplies provides high quality poker chips, chip cases and carousels, card shufflers and poker accessories at great wholesale and cheap prices. Ultimate Poker Supplies carries poker, clay, casino & customized chips, KEM & COPAG cards, shufflers, cases, DVD's, and Blackjack supplies. Poker chip suppliers list.
One reason Planning Poker leads to better estimates is because it brings together multiple expert opinions. Because these experts form a cross-functional team from all disciplines on a software project, they are better suited to the estimation task than anyone else.
Scrum Planning Poker
After completing a thorough review of the literature on software estimation, Magne Jørgensen, Ph.D., of the Simula Research Lab concluded that 'the people most competent in solving the task should estimate it.'
Second, a lively dialogue ensues during poker planning, and estimators are called upon by their peers to justify their estimates. Researchers have found that this improves estimate accuracy, especially on items with a lot of uncertainty as we find on most software projects.
Further, being asked to justify estimates has also been shown to result in estimates that better compensate for missing information. This is important on an agile project because the user stories being estimated are often intentionally vague.
Scrum Story Points Definition
Additionally, studies have shown that averaging individual estimates during agile estimating and planning leads to better results as do group discussions of estimates.
How can I get Planning Poker cards?
Planning Poker cards are available in the Mountain Goat Software store. Mountain Goat Software's branded Planning Poker cards are sold at cost as a courtesy to the agile community.
Our full-color cards are the absolute highest-quality cards available anywhere. They are manufactured by the same company that prints many of the world's most popular playing card brands, including Bicycle, Bee, and the World Poker Tour.
We also offer royalty-free licenses to organizations that wish to produce their own cards. The license is available here: https://www.mountaingoatsoftware.com/agile/planning-poker/license
Scrum Poker Planning Cards
Recommended Resources Related To Planning Poker
- How Can We Get the Best Estimates of Story Size?
- The Best Way to Establish a Baseline When Playing Planning Poker
- Don't Average During Planning Poker
- Agile Estimating
Courses Related To Planning Poker
Scrum Foundations Video Series
All the foundational knowledge of Scrum including: the framework, values, different roles, meetings, backlogs, and improving efficiency & quality.